Schizophrenia

What is Schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is a very severe mental health issue that impacts how your brain works. It alters the normal brain activity, which distorts your cognition, memories, and senses. You face trouble organizing your thoughts and have disrupted behavior that makes you vulnerable to injuries or other illnesses. Schizophrenia causes psychosis, which brings forth a misperception of reality. This seriously presents a challenge in all areas of your daily life, as well as your relationships and social interactions.

Schizophrenia Symptoms
Many schizophrenic individuals do not notice or sense what they are going through. People around them might recognize what’s wrong with them. Schizophrenia symptoms are divided into positive and negative symptoms.
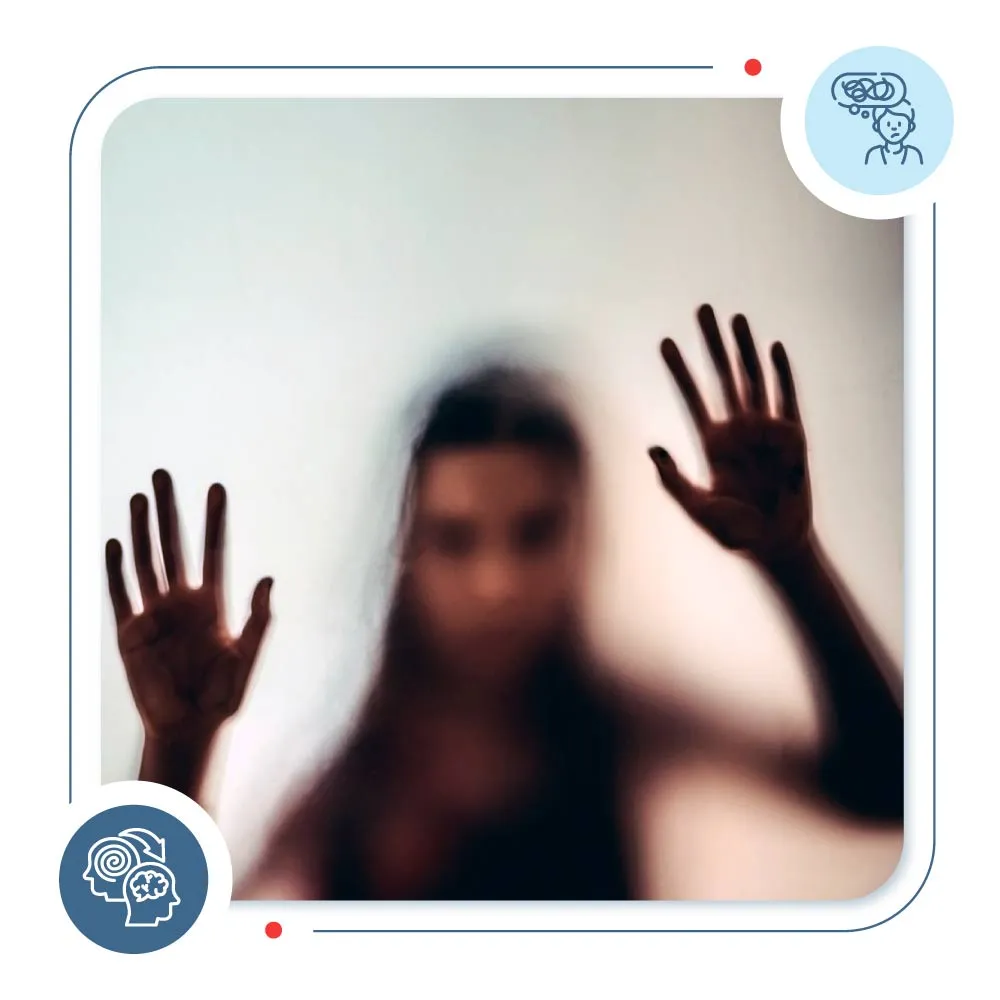


Positive symptoms
Positive symptoms mean you sense abnormal elements that are not normally present at all. Positive refers to the addition of something:
Hallucinations
You keep experiencing things which are not real, e.g., you hear sounds nobody else can hear, or see things that others deny to be there.
Delusions
These are your unchanging, permanent, wrong beliefs, e.g., you hold extraordinary supernatural powers or you are being controlled by others, e.g., aliens. Delusions are a hallmark of schizophrenia symptoms.
Paranoia
It makes you feel distrustful of others. You think they are plotting against you or trying to harm you physically.
Catatonia
Your brain doesn’t control muscle movements the way it should. You either make a lot of unnecessary movements (e.g., fidgeting or spinning) or remain completely still for hours. Your friends or family might notice you standing in some awkward posture without support for a longer duration.
Disorganized cognition and speech
You struggle with streamlining your thoughts while speaking. You might keep hopping around topics, making people unable to get what you are saying.
Anomalous behavior
You start laughing or crying at situations that do not warrant such responses.
Negative symptoms
Negative symptoms imply a deficit of normal functioning in your physical or emotional state. Negative refers to missing something:
Emotionally less expressive, e.g., absence of facial expressions, no tone in speech
Not motivated to do purposeful activities or maintain personal hygiene
Not experiencing pleasure
Isolating yourself from social interactions
Causes of Schizophrenia
Researchers are unable to find the exact cause of Schizophrenia. That is why no accurate schizophrenia cure has been evolved yet. Ongoing researches, though, point to several risk factors that might result in this mental health issue, which include:
- If you have a known family history of this mental health issue, especially with your first-degree relative suffering from schizophrenia.
- If you have specific abnormalities in your brain structure. Researchers suggest that such variations in the anatomy of your brain can be seen through neuroimaging techniques. Nonetheless, actual schizophrenia brain malformations have not yet been discovered clearly.
- Some neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and glutamate, govern your brain to process information and emotions. You tend to get schizophrenic if the levels of these chemicals change in your brain.
- If you were into mind-altering drug usage in your teenage years or adolescence.
- If you experience significant Stress or trauma, especially in your childhood.

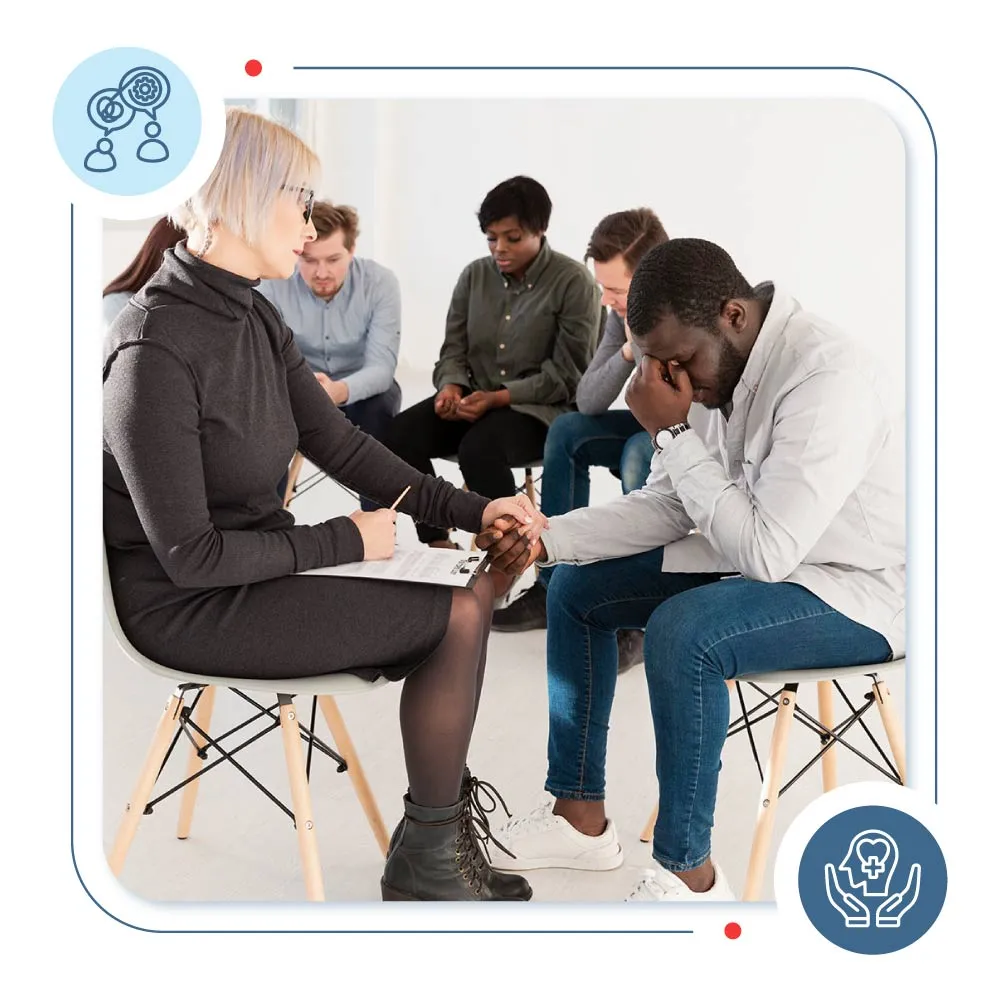
Treatment of Schizophrenia
Mid Cities Psychiatry always delivers evidence-based mental health services. Our experts treat all kinds of schizophrenia symptoms and offer you comprehensive mental health therapy options.
- Psychiatric Medications
Antipsychotics - Psychotherapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy CBT - Innovative Techniques
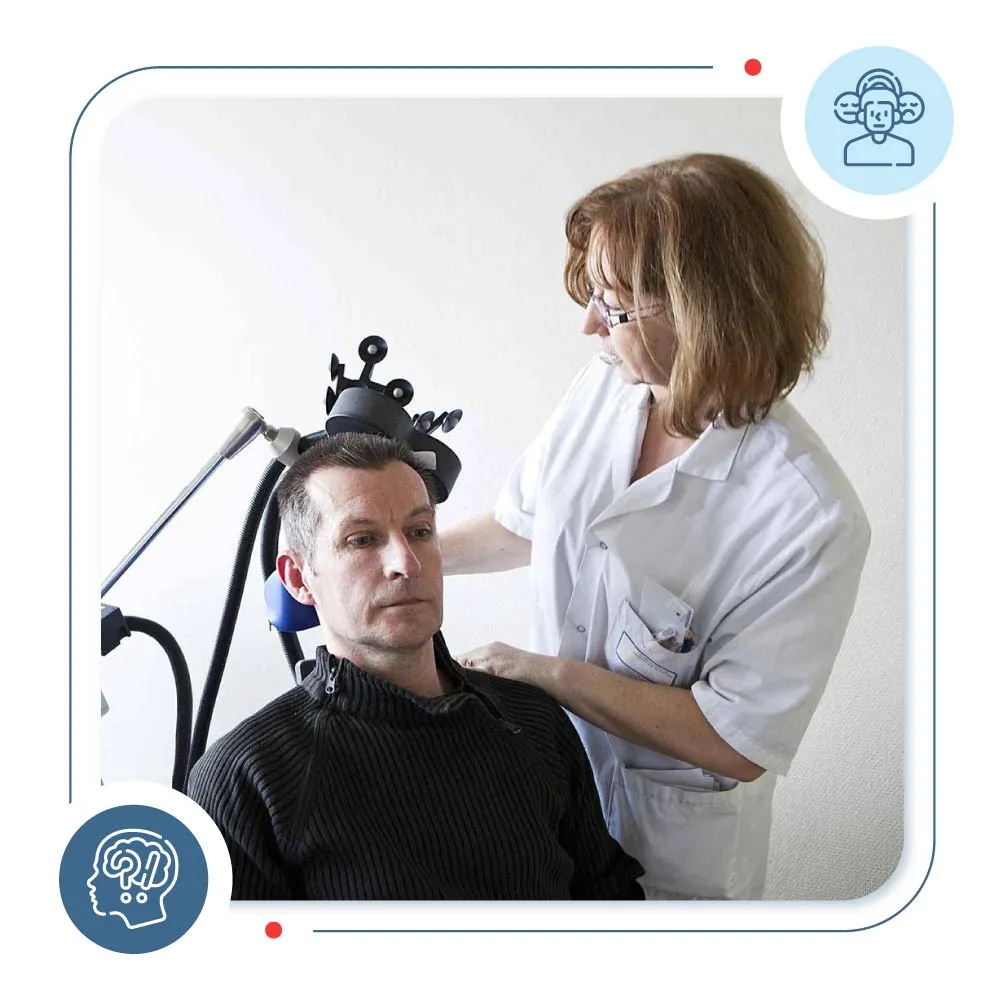
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation TMS therapy , Electroconvulsive Therapy ECT



Are there any types of Schizophrenia?
Formerly, schizophrenia was designated under various types, which were not that practical for directing proper treatment. Under DSM-5 criteria established by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) for diagnosing mental health issues, schizophrenia is now viewed as a ‘Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic Disorders’. Nonetheless, the characteristics of schizophrenia symptoms of previous types are still part of the criteria for concluding.

FAQs
01
How are Schizophrenia and Lack of Insight (Anosognosia) related?
Anosognosia makes you clueless about your mental health disorder. You don’t acknowledge your condition and consider yourself completely fine. It is just a symptom that you show, and not a separate disorder. People with mental health conditions, including schizophrenia, may develop Anosognosia without knowing it.
02
When and how am I given a schizophrenia diagnosis?
Psychiatrists base their schizophrenia diagnosis on DSM-5 criteria. You must show 2 or more of these signs, with at least 1 being out of (1-3), to be schizophrenic.
- Delusion
- Hallucinations
- Disorganized speech
- Catatonia
- Anomalous behavior
- Negative symptoms
Your schizophrenia symptoms must last for a minimum of 6 months and remain active for at least 1 month.
03
What is the long-term prognosis for schizophrenia?
Experts have not found a complete schizophrenia cure yet. Your condition may never disappear completely. When you accept your schizophrenia diagnosis and start getting help, you can enjoy better mental health while living a fulfilling life.
04
Where can I discover more schizophrenia information?
The National Institute of Mental Health features official information about schizophrenia through its platform. Visit their website without charge to read recent news and explore research results about schizophrenia.
05
Why are schizophrenic individuals more prone to other medical conditions as well?
Schizophrenia patients are more at risk of health problems because of prescription drug consequences, plus their minimal attention to self-care, combined with unhealthy behavior patterns. Stress and serious mental health problems make it harder for someone with schizophrenia to take care of their overall well-being.
Real Stories, Real Recovery





We provide a comprehensive care provision for the most common mental issues people struggle with, such as PTSD, ADHD, OCD, anxiety, depression, sleep disorder, schizophrenia, and numerous other mental health conditions.





